Plastic Chrome Plating

Auto Interior – Ring
Auto Interior – Bright Chrome Knurled Ring
Auto Interior – Dashboard
Plastic Chrome Plating Manufacturer for Automotive, Appliance Components
Your Blueprint for Mass Production Success
Our plastic chroming project execution is a disciplined, phase-gated process designed to eliminate uncertainty and ensure a seamless transition to mass production.
1. Feasibility & Tooling Kick-off: The journey begins only after a thorough assessment confirms we can manufacture your plastic plated parts to all specifications. Upon your approval, we immediately commence precision tool construction.
2. Iterative Refinement & Validation: Approximately one month later, we deliver the First Off Tool (FOT) samples and take them to trial plating. This initiates a critical “Test-Iterate-Approve” cycle. We focus first on achieving dimensional and functional integrity, then meticulously refine the surface appearance to match your master sample. We are prepared to conduct multiple sampling rounds (T1 to Tn) — treating each iteration as a targeted problem-solving step — until the parts pass all dimensional, cosmetic, and performance validations.
3. Launch for Sustainable Mass Production: This rigorous development phase directly solves the core trilogy of scaling challenges: scaling up volume without compromising quality, enduring real-world automotive conditions, and stabilizing output for batch-to-batch uniformity. The result is a production-ready process that delivers the rugged reliability and consistent quality your high-volume automotive projects demand.
OEM surface finishing solutions for ABS, PC and PC+ABS parts.
For over 50 years CheeYuen delivers high-performance surface finishes tailored for engineering plastics like ABS, PC, and PC+ABS. We specialize in chrome plating plastic and custom finishes that meet strict OEM requirements in automotive, appliance, and sanitary industries.
Our Solutions:
- Material-Specific Processes: Optimized pre-treatment and plating for adhesion, coverage, and thermal resistance.
- Customization: Wide range of color(Bright Chrome, Satin Chrome, Black Chrome, Satin Black Chrome), textures, and effects, including eco-friendly trivalent chromium plating (Cr3+).
- Quality & Compliance: IATF 16949 and ISO 9001 certified, with RoHS/REACH compliance.
We provide reliable, production-ready finishes—from prototyping to volume manufacturing.
Automotive & Home Appliance Project Experience
By partnering with a leading cockpit systems supplier (Marili), we helped increase the yield rate for a specific high-end model’s air vents by 15%, while also generating annual cost savings of 500,000 RMB for them through a VAVE (Value Analysis/Value Engineering) project.
In the home appliance sector, we leveraged our expertise in cost-effective tooling design for a coffee machine knob, which secured the trust of Delonghi, a leading European high-end coffee machine manufacturer.
Learn More About Our Plastic Chrome Plating Services
Write your message here and send it to us
Excellent Plastic Chrome Plating Service
At CheeYuen, we provide high-quality plastic chrome plating solutions for automotive, appliance, and bathroom fixture manufacturers. Our expertise ensures durable, visually appealing chrome finishes for a variety of plastic components, enhancing both their aesthetics and functionality.
With over 50 years of experience, we offer custom solutions to meet diverse industry needs, using eco-friendly processes that comply with international standards. Whether it’s high-gloss finishes for automotive parts, stylish coatings for appliances, or corrosion-resistant layers for bathroom fixtures, we deliver precision and reliability on time, every time.
Typical Parts We Plate in Mass Production
Coffee Machine – Bright Chrome Cover
Whirlpool Oven – Black Chrome Knob
Home Appliance – Bright Chrome Faucet
Auto Part – Satin Chrome – Right &Left Lock Bezel
Home Appliance – Loop Bezel Knob
Washing Machine – Handle Trim
How Your Plastic Chrome Plating Project Works
We support OEM manufacturing projects only. Every part is produced based on drawings, specifications, and volume plans — not as retail items.
Step 1 – Requirement Review & DFM & Mold Construction
We conduct a thorough drawing review and material confirmation (e.g., ABS, PC, PC+ABS). The process focuses on evaluating the design for manufacturability and aligning with your surface and appearance targets.
Step 2 – Sampling & Approval
Prototype plating is performed for real-world testing of adhesion and appearance. Production proceeds only after formal customer sign-off on the submitted samples.
Step 3 – Process Engineering
This phase finalizes the production setup, including bath formulation, custom jig design, and precise parameter setup for the plating line to ensure quality consistency.
Step 4 – Mass Production
Mass production runs on our in-house plating lines. We utilize SPC for real-time monitoring and maintain full batch traceability throughout the process.
Step 5 – Quality Control & Delivery
All batches undergo final inspections (cross-hatch, salt spray, visual). Approved parts are then securely packaged and prepared for export delivery.
Plastic Chrome Products (Satin Chrome)
BMW – Operating Element Rocker
Auto Part – Satin Chrome Gear Trim
Auto Part – Door Handle
Plastic Plating Products (Bright Nickel)
Home Appliance – Bezel Knob
Home Appliance – Brushed Bright Nickel Knob
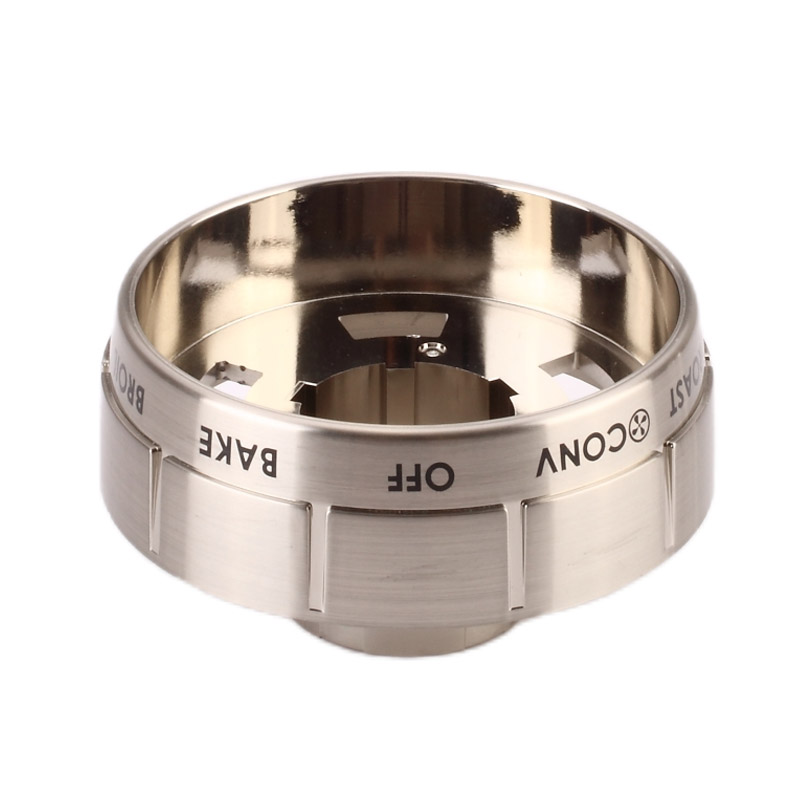

Home Appliance – Electroplatig Oven Bezel Cover
Plastic Chrome Plating (Trivalent Chrome)
Black Chrome Handle
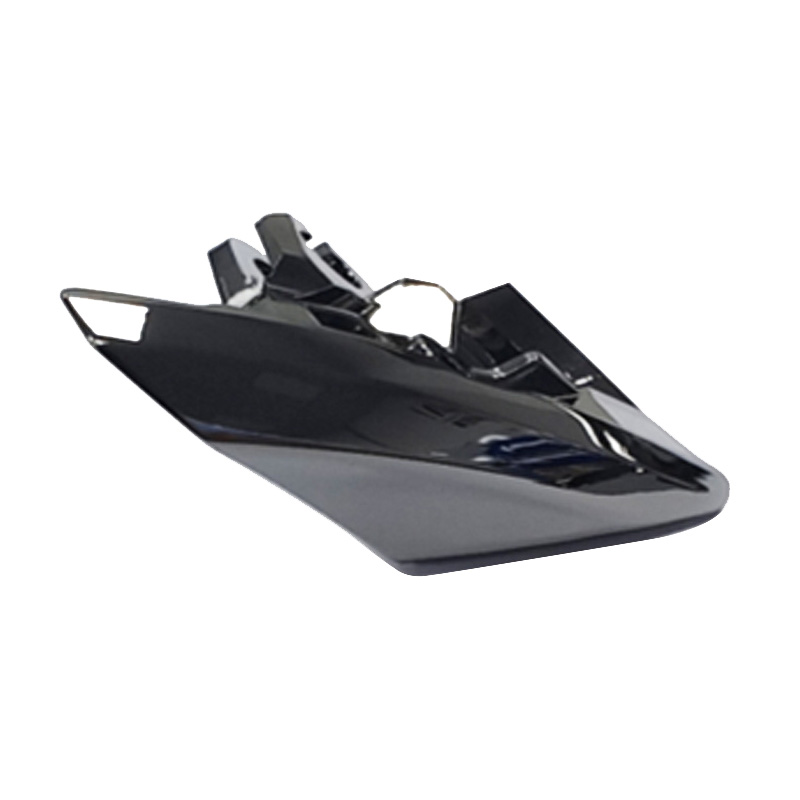

Auto Door Knob

Automotive Door Trim
Chrome Plating On Plastic Process
To prepare plastic for chrome plating, it undergoes roughening and activation as key pre-treatment steps. The critical step is electroless plating, where a thin nickel layer (a few microns thick) is applied to create a conductive base for copper and nickel plating.
Plastic Plating Line Capability
We operate two state-of-the-art plating lines: an automatic plating line and a circular plating line, both designed to handle a wide range of parts for plastic chrome plating.
The plating tank for automatic plating line measures 300*120*150 cm, large enough to accommodate not only small parts but also larger components such as grilles, trims, and other automotive or home appliance parts. The plating tank for the circular plating line measures 75*90*150 cm, ideal for smaller and medium-sized parts like logos, knobs, levers, and similar items.
With a plating capacity of 1,500,000 square meters per year, our production lines are built to deliver high volumes of plastic chrome plating while maintaining precision and quality.
Our plating lines are equipped with world-class control systems and high-performance filters, including the renowned German AUCOS control system, which features fixed pace and mixing processes, Dutch MeFiag filters, and Italian CRS rectifiers. These advanced technologies ensure consistency and precision across all of our plastic chrome plating projects.
We use electroplating chemicals from trusted suppliers such as MacDermid-Enthone, Atotech, and JCU, ensuring high-quality results in applications across a wide range of industries. Our plastic chrome plating is commonly applied to automotive, home appliance, and bathroom parts, including emblems, handles, trims, lamp shells, knobs, buttons, and more.
Quality Testing
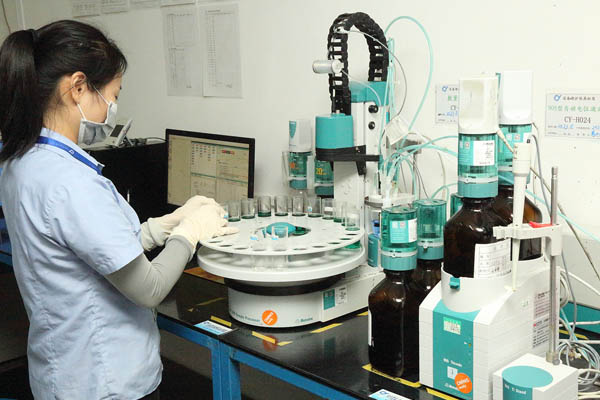

To ensure product quality and boost customer confidence, we have a comprehensive inspection system in place that tests and analyzes every process.

54 years of experience in the plastic chrome plating industry
IATF 16949, ISO 9001, ISO 14001 Certified
One stop solution from tool design to finished parts.

Professional plating technical team
CONTACT US
Write your message here and send it to us
Main Customers




















Credentials
The company has passed the ISO9001 quality management system and ISO14001 environmental management system certifications, as well as the ISO/IATF16949 automotive product quality management system certification.

D-U-N-S Certification

IATF 16949 for Automotive Industry

ISO9001 for Quality Management System Standard

Iso14001 for Environment Management System Standard

Awarded by Continetal Customer

Awarded by LIXIL
FAQ | Plastic Chrome Plating
What Types of Plastic Can Be Chrome Plated?
We specialize in plating the following plastic materials:
- ABS
- PC-ABS
- Polypropylene
These materials are commonly used in automotive, appliance, and bathroom products, offering excellent adhesion and durability for chrome finishes.
What Finishes Do You Offer?
We provide a variety of finishes to meet unique design requirements:
- High-gloss
- Matte
- Satin
Perfect for automotive trims, appliance components, and bathroom fixtures.
How Durable is Chrome Plating on Plastic?
Our chrome plating is engineered to withstand:
- Temperature changes
- Moisture exposure
- Corrosion
This makes it ideal for outdoor automotive parts, kitchen appliances, and bathroom fixtures.
Is Your Chrome Plating Eco-Friendly?
Yes! We use sustainable, eco-friendly processes and materials that adhere to international environmental standards without compromising quality.
What’s the Typical Turnaround Time?
Most orders are completed within 2-4 weeks, depending on complexity and quantity. We prioritize efficient production schedules to align with your timelines.
Can You Handle Large Orders?
Our advanced facilities are fully equipped to manage bulk production for industries like automotive and home appliances, ensuring consistency and precision in every piece.
Quality Assurance on Every Component
Every chrome-plated product undergoes strict quality control, including:
- Adhesion testing
- Surface finish inspections
- Corrosion resistance evaluations
We ensure each product meets the highest quality standards.
How Does Plastic Chrome Plating Compare to Metal Chrome Plating?
Plastic chrome plating offers:
- Similar premium aesthetics to metal chrome plating
- Lightweight properties
- Cost-effectiveness
- Rust resistance
This makes it a superior choice for industries such as automotive and household applications.













